There are no UNIX Terminal commands that can do all of this in one go. You will need to script it and then run the script with the folder containing the MP3 files. This script is recursive so it will plumb a folder hierarchy.
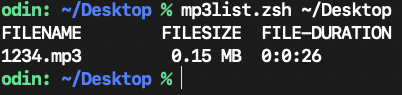
Sample:
Copy the following code into (ideally) a programmer's editor (e.g. BBEdit, macVIM, etc.) and save as plain text (e.g. mp3list.zsh) to your Desktop, though it just needs to be in your PATH (e.g. /usr/local/bin). Launch the Terminal application and enter the following:
cd ~/Desktop
chmod +x ./mp3list.zsh
./mp3list.zsh folderpath
In proper UNIX tradition, you can redirect the output of this script to a text file:
./mp3list.zsh folderpath > ~/Desktop/mp3list.txt
Code:
#!/bin/zsh
: <<"COMMENT"
List each MP3 file's name, filesize, and duration as hh:mm:ss instead of a
decimal duration. This script takes a single folder as a command line argument
and recursively hunts for all MP3 files in it.
Usage: mp3list.zsh ~/folderpath
Output:
FILENAME FILESIZE FILE-DURATION
1234.mp3 0.15 MB 0h:0m:26s
Tested: macOS Sequoia v15.2, Monterey 12.7.6
VikingOSX, 2024-12-18, Apple Support Communities, No warranties whatsoever.
COMMENT
# no script argument or no folder passed
[[ $# = 1 || -d "${1}" ]] || exit 1
# if there are no .mp3 files present in the provided folder hierarchy then exit'
files=( "${1}"/**/*.mp3(.N) )
(( $#files )) || exit 1
# since .mp3 files are present in provided folder, we can print the header
printf 'FILENAME\tFILESIZE FILE-DURATION\n'
for f in "${1}"/**/*.mp3(.N);
do
ds=$(/usr/bin/afinfo "${f}" | awk '/duration:/ { printf "%4.2f", $3}')
fs=$(/usr/bin/stat -f '%z' "${f}")
# just the filename and extension
fn="${f:t}"
# perform the MB calculation for file size
fmb=$(bc -l <<<"scale=3;${fs}/(1024 * 1024)")
# and print out results for this mp3 file iteration including duration
printf '%s\t%5.2f MB %d:%d:%d\n' "${fn}" ${fmb} $(($ds/3600)) $(($ds%3600/60)) $(($ds%60))
done
unset files
exit 0